Guide to Mutual Fund Investments
- 25 October 2019 | 1678 Views | By Abhinav Mishra

Mutual funds have established as a globally recognizable investment instrument. With underlying varying from international investments, to debts, government securities, equity and even specific sectors, mutual funds have a solution for all sorts of investment queries.
Investors can not only time their investments, but can also decide on the amount to be invested, frequency of investment and even fund allocation as per risk appetite.
As told above, mutual funds do carry multiple investment methods, which range from lump sum, SIP, SWP, STP, SWAP and several other methods. While lump sum is not the preferable choice of retail investors, the latter are indeed getting popular everyday, among investors of all ages and risk appetite. Owing to the several methods that exist, confusion among investors is quite common.
In this article, we shall explore the several investment methods via one can start saving or investing via mutual funds.
As an investor one is always worried as to where to invest one’s hard-earned money to have the least risk and get the maximum returns. The investor finds himself stuck when it comes to making an investment decision as there are hundreds and thousands of options available to invest in but he/she is unaware of the risks and returns attached to it. Building wealth necessitates financial discipline and a long-term sphere for investing. In today’s time, it is very important to have proper and adequate financial planning so as to create a financial cushion to achieve one’s long term and short term objectives. To achieve your financial goals, one needs to make the right investment choices and invest systematically and smartly. A proper investment planning requires discipline and regularity so that the volatility of the markets can be tapped on and with the right choices of investment, one can make their portfolio risk-neutral.
Systematic investment choices can help individuals with less knowledge about the markets achieve better returns. To get a basic insight into some types of systematic investments lets understand the 3 main types of Systematic investment transactions as under:
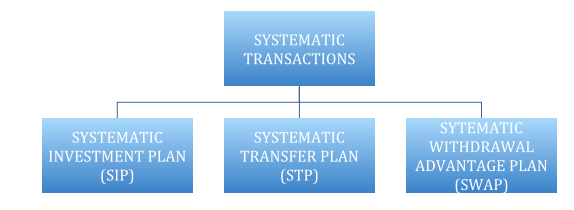
Now let us understand each of these in some details.
SYSTEMATIC INVESTMENT PLAN (SIP)
Systematic Investment Plans have gained massive popularity over the last decade, particularly due to the convenience, financial discipline and safety they provide. A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is basically a disciplined approach to invest in mutual funds wherein one commits to invest a fixed amount on a periodical basis. A SIP enables the investor to break their investments over a yearly or a quarterly or a monthly period. One can either give post-dated cheques or easily opt for the electronic clearing service (ECS) under which your bank will automatically debit the given amount on a specific date, to be invested in the mutual fund scheme.
SIPs are ideal for investors who don’t have the market expertise, a big lump sum to be invested immediately or the time to constantly monitor their investments. Through SIPs, investors can easily apply the power of compounding on their investments and build a substantial corpus over a period of time.
SIP’s can be of the following types:
Flexi SIP
Under this scheme, the investor is flexible and not bound to pay a fixed amount of installment. This type of SIP provides the facility to increase or decrease the SIP amount as per the cash flow of the investor. So, when an investor faces any kind of cash crisis due to some reasons, he/she can skip payment of few SIP installments till the financial situation returns to normal. On the contrary, if an investor receives any bonus or makes some extra gain, he can deposit the full or part of the amount into the SIP account.
A Flexi SIP allows the investor to vary the amount of their investments every month. If they do not want to invest a fixed amount and prefer more control over their investments, they can set up a Flexi SIP to fulfill this. They will have to specify a default amount for the investments. If they do not want to change the SIP amount nearing the SIP installment date, the default amount selected by them will be invested.
Flexible SIP plans are usually associated to a key ratio. Once the market goes down and it hits the pre-fixed level or below the key ratio, the Flexi SIPs kick in and the investments go up automatically.
Top-up SIP
Top-up SIP is a facility that allows investors to increase the monthly investment amount periodically as a percentage of the existing SIP installment or increase it by an absolute amount. Under the SIP Top-Up facility, the unitholders are offered the following facilities:
a) Fixed Amount top-up i.e. to increase the amount of the SIP Installment by a fixed amount of the previous installment at each specified pre-defined intervals, or
b) Percentage Top-up i.e. to increase the amount of the SIP Installment by a specific percentage of the previous installment at each specified pre-defined intervals.
Perpetual SIP
Normally an investor signs up the SIP mandate for a fixed period of time, say, 1 year or 3 years or 5 years and so on, but if the investor does not enter any end date in the SIP mandate, it is regarded to be a perpetual SIP. This leaves the option open for the investor to redeem the fund at the time of his/her choice or when their financial goals are achieved.
Trigger SIP
This type of SIP is better suited for investors who have sound knowledge and awareness of the financial markets. Under the trigger SIP, investors can set a target based on pre-specified date, price, NAV and index level. If, for instance, you know that a certain kind of government policy will be in force in a couple of days and that will affect the index crossing up to a certain mark, you can set it as a trigger date.
Advantages of SIP
There are numerous benefits of investing in SIP which include:
- Disciplined Saving habit in investors: For any investment to be fruitful, discipline is required. By investing through SIP, investors commit to save regularly, and every investment takes them a step closer to reaching their financial objectives and goals.
- Convenience: Investing through SIP is a hassle-free process. Investors can instruct their bank to facilitate auto-debits from their account for payment of installments without having to worry about remembering the time of installments.
- Rupee cost averaging: When investors invest a fixed amount of money every month through SIP, they will notice that more units or stocks are purchased when the price of the investment goes down. This brings down the average cost of buying the financial asset over time.
- Benefits of compounding are reaped: A small sum of money invested through SIP on a regular basis can grow into a significantly large amount. Through the power of compounding, the interest also earns interest, allowing the investors to fetch a substantial amount of wealth.
SIP is a simple, convenient and affordable way to invest for the future. With as low as 1,000 every month, it’s an efficient method to invest in the growth potential of mutual funds.
SYSTEMATIC TRANSFER PLAN (STP)
Systematic Transfer Plan (STP) is a stratagem where an investor transfers a fixed amount of money from a Source scheme to a Target scheme. Given the volatility in the equity market people having a huge amount of cash invest it into a debt fund and then gives STP instructions to transfer a fixed amount at a fixed interval for a fixed period in one or more equity mutual fund in parts. As of now, the transfer can happen only between mutual funds of the same fund house and not inter-fund houses, i.e., if you invest in HDFC mutual fund, you can transfer into another HDFC mutual fund only.
- Fixed STP
Under this kind of STP, the amount to transfer periodically is fixed. The investor can decide on the amount as per his financial goal and apply for the same.
- Capital Appreciation
For this kind of STP, only the capital appreciated in the scheme is transferred from source fund to the target fund and the capital part remains safe in the same fund.
- Flexi STP
As the name suggests, Flexi STP is flexible. This means that the investor can choose to transfer a varied amount from the source fund to the target fund. Investors mostly want the amount as per the market rate fluctuations. For instance, if the Net Asset Value of the destination fund dips, they can increase the amount and vice versa.
Flexi STP banks upon the fluctuation in market, which creates dip in NAV of the mutual funds.
BENEFITS OF SYSTEMATIC TRANSFER PLAN:
- Balancing investments – STP helps to rebalance the portfolio by allotting investments from debt to equity or vice versa as per the market demands.
- Averaging of Cost – STP has some essential features of the Systematic Investment Plan (SIP). Since it is comparable to SIP, STP also helps in Rupee Cost Averaging hence averaging the overall cost of investment.
- Aims for Higher Return – Money invested in debt fund normally yields normal returns till the time it is transferred to an equity fund. The returns in debt funds are usually higher than those in the savings bank account and it aims to ensure relatively superior performance.
STP is predominantly suitable to investors who have lump sum money and wish to invest in equity funds but are mistrustful of timing the market. They can then choose to invest the lump sum money in a liquid or debt fund and use the STP option to systematically transfer a fixed amount of money at regular intervals into the target equity fund.
SYSTEMATIC WITHDRAWAL PLAN (SWAP)
A SWAP allows an investor to withdraw a pre-determined sum of money and units from the fund account at pre-defined regular intervals. It permits investors a certain level of independence from market instability and helps in evading unfavorable market timing. The investor can reinvest the redeemed cash from this scheme in another portfolio or use it as a source of their regular income. It can be of the following two types:
Fixed Withdrawal: Under a fixed withdrawal option, the investor specifies the amount that he wants to withdraw from his investment on a monthly/quarterly basis.
Appreciation Withdrawal: In an appreciation withdrawal option, the investor withdraws only the appreciated amount over and above the principal invested on a monthly/quarterly basis.
Advantages of SWAP
-
- Liquidity: A SWAP option can help an investor who needs liquidity as it permits them to access their money precisely when they need it to meet their needs.
- Regular Income: SWAP helps in creating a regular flow of money from investments on a periodic basis i.e. on a monthly or quarterly basis.
- Tax Benefit: Instead of selling all the units at once, segregating the income across multiple intervals can lower the total tax. It is a tax-effective way of getting regular income.
- Avoid market fluctuations: It saves an investor from market fluctuations and risks associated as regular withdrawal averages out return value.
Conclusive words
When an investor buys stocks, the most critical factor they need to ensure is that they choose the right one, otherwise, they could end up with an underperforming investment, or worse yet, an investment where they might suffer a loss. The same holds true when they invest in a mutual fund.
Identifying your investment horizon as well as risk profile will help you figure what kind of fund will be the most suitable for you. Say, if you do not wish to take on much risk and want consistent returns, debt funds might be a better option for you. But if you want to stay invested for the long term and are comfortable with market volatility, then equity funds may be more suited for you.
After you have identified the kind of investment avenue you want to go for, you need to find out which scheme would be a good option for you. It is advisable to go with older funds since they have a historical track record for investors to analyze and take a cue from. It is also suggested to maintain a conservative approach when stating the expected return. Do not go overboard just because one scheme has had an outstanding performance for a year; rather you need to analyze historical figures of a broader time frame.
There is no doubt that mutual funds play multiple roles for a retail investor.
(a) For a young investor, mutual funds are a tool for capital appreciation and tax saving. He expects to beat inflation and prepare for major expenses like buying a car or a house.
(b) For a middle aged investors, mutual funds are an investment vehicle to accumulate savings for retirement purposes and, also act as a tax saving instrument.
(c) For senior citizens, mutual funds are an easy option to park savings for managing day to day living expenses, without losing on interest expenses.
In coherence with their needs, we have mutual funds which range from equity, debt, arbitrage and even government securities. There are liquid funds, equity funds, international funds, and tax savers, serving as major examples of mutual funds.
All one needs is a helpful investment guide to make sure his investment gets as close as possible to the approximated returns.